Bitcoin halving dates represent some of the most important days in the crypto ecosystem. They usually trigger heightened attention from traders and investors, but the mainstream press as well, as they historically led to higher Bitcoin prices and an upward move for the entire crypto market.
A Bitcoin halving event takes place every four years, reducing the block reward for miners by 50%. The first one was on November 28, 2012, when the BTC block reward was cut from 50 coins to 25 coins per block.
Find out when the next Bitcoin halving will take place and why these events matter so much for the crypto industry.
What is the Bitcoin Halving
On January 3, 2009, the Bitcoin network was created by Satoshi Nakamoto when he mined the starting block of the chain which is called the Genesis Block.
The first digital asset in the world has one critical pre-programmed feature: the reward that miners receive for validating transactions into a block is not a permanent one.
Bitcoin halving occurs after every 210,000 blocks are mined, an event that takes place once every four years, and slashes miners’ revenue to half.
This event leads to the following results:
- Lowering the supply of new Bitcoins entering the market
- Increasing scarcity of coins
- Rasing Bitcoin’s market price
Block rewards are included in the blockchain’s automatic process that validates transactions and opens new blocks. Miners, the participants who compete in a race to solve cryptographic puzzles, receive new Bitcoins if they’re the first to solve them.
The block is added to the blockchain, miners receive a reward, and the network starts another race of solving cryptographic puzzles.
Why Does the Bitcoin Halving Occur
Bitcoin halving events occur to fulfill Satoshi Nakamoto’s vision of creating a deflationary currency.
Bitcoin is very different from fiat currency, and the main feature that makes it unique is that, unlike fiat, Bitcoin has a fixed supply capped at 21 million coins. This means that there will never be more than 21 million Bitcoins in existence.
This controlled issuance can be achieved via halving events that lead to a gradually decreasing rate of new Bitcoins entering circulation. In other words, it limits supply growth.
Bitcoin Deflationary Mechanisms vs. Fiat Inflationary Nature
Bitcoin’s deflationary mechanisms are in a strong contrast with fiat’s inflationary nature.
In the case of fiat currencies, increasing money supply can lead to decreased purchasing power.
Bitcoin’s halving ensures scarcity and this can enhance its value over time, protecting against inflation, the exact opposite of how fiat currencies work.
This deflationary design created by Satoshi Nakamoto for Bitcoin ensures that it will create a digital asset that retains its value in the long term. It makes Bitcoin a unique and revolutionary form of currency in the global financial system.
When Did the Previous Bitcoin Halvings Occur
Until now, four Bitcoin halving events have taken place. Nasdaq details Bitcoin halving cycles by using “Epochs” and revealing the Bitcoin miner rewards for the previous and future epochs.
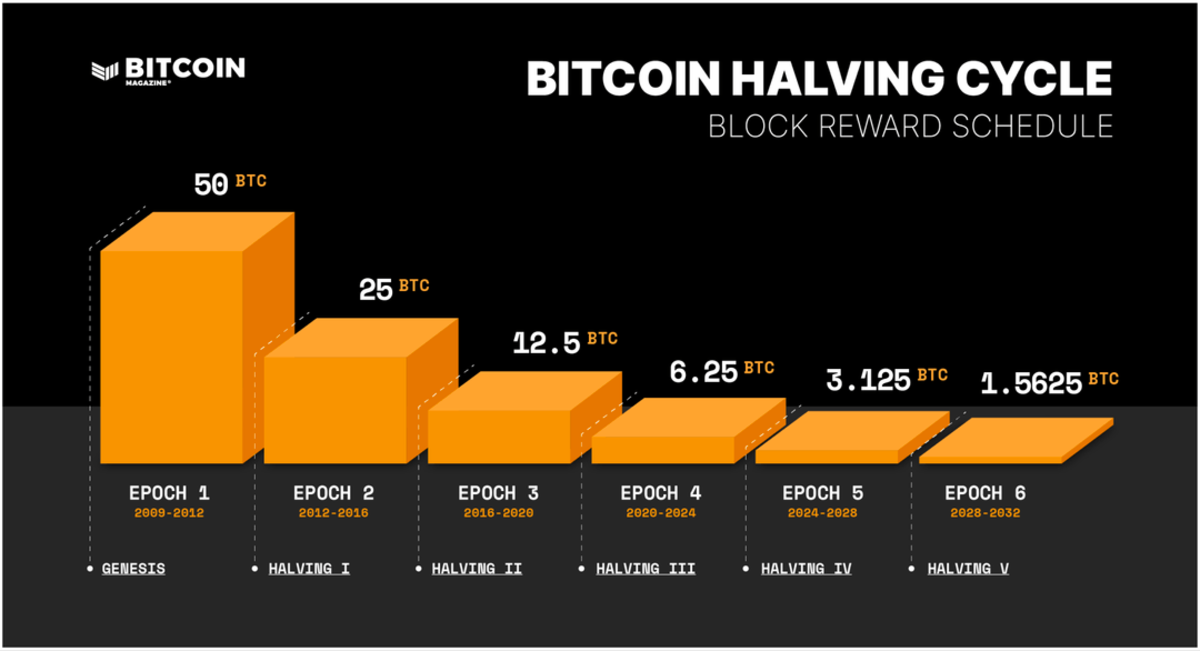
1. Bitcoin 1st Halving – November 28, 2012
On November 28, 2012, the first Bitcoin halving event took place. The event was pivotal for early adopters and miners, and it marked a significant shift in the Bitcoin ecosystem.
Here are the key points of the 2012 Bitcoin halving event:
- Bitcoin halving: at block 210,000
- Bitcoin reward per block before the halving: 50 BTC
- Bitcoin reward per block following the halving: 25 BTC
- Bitcoin price on halving day: Around $12
- Bitcoin price 150 days after the halving event: $127
While miners’ rewards were halved, they experienced a direct impact on their profitability. But this also meant that Bitcoin’s issuance rate decreased, boosting its scarcity.
Within the following year, Bitcoin’s price surged to around $1,000.
This price increase validated Satoshi Nakamoto’s envisioned model and attracted more attention and investment into the crypto industry.
The first Bitcoin halving event set a precedent for the following ones, highlighting the strong potential to significantly influence Bitcoin’s market dynamics and reinforcing the long-term value proposition of Bitcoin as a scarce digital asset.
2. Bitcoin 2nd Halving – July 9, 2016
On July 9, 2016, the second Bitcoin halving event took place. The market’s reaction was initially muted, with Bitcoin’s price hovering close to $650.
However, this halving set the stage for a significant bull run, and over the next 18 months, BTC’s price surged reaching almost $20,000 in December 2017.
Here are the key points of the 2016 Bitcoin halving event:
- Bitcoin halving: at block 420,000
- Bitcoin reward per block before the halving: 25 BTC
- Bitcoin reward per block following the halving: 12.5 BTC
- Bitcoin price on halving day: Around $650
- Bitcoin price 150 days after the halving event: $758
The halving attracted more institutional interest and mainstream media attention.
The long-term effects included the following:
- Increased network security
- Greater miner efficiency
- Reinforced perception of Bitcoin as a store of value
3. Bitcoin 3rd Halving – May 11, 2020
On May 11, 2020, the third Bitcoin halving event took place, as speculation grew about institutional adoption and Bitcoin as an inflation hedge.
Following the event, the price surged, and it kicked off another bull run in 2021.
Here are the key points of the 2020 Bitcoin halving event:
- Bitcoin halving: At block 630,000
- Bitcoin reward per block before the halving: 12.5 BTC
- Bitcoin reward per block following the halving: 6.25 BTC
- Bitcoin price on halving day: Around $8,820
- Bitcoin price 150 days after the halving event: $10,943
Immediately following the halving event, Bitcoin’s price saw modest fluctuations, with Bitcoin reaching a new ATH of over $60,000 by April 2021.
The halving event boosted Bitcoin’s scarcity narrative, attracting increased institutional investment and widespread adoption.
The event increased mining competition and efficiency, securing the network further, reinforcing Bitcoin’s role as digital gold, and solidifying its place in the global financial landscape.
4. Bitcoin 4th Halving – April 20, 2024
On April 20, 2024, the fourth Bitcoin halving event took place, amidst growing anticipation regarding the digital asset’s evolving role in the global financial system.
Here are the key points of the 2024 Bitcoin halving event:
- Bitcoin halving: At block 840,000
- Bitcoin reward per block before the halving: 6.25 BTC
- Bitcoin reward per block following the halving: 3.125 BTC
- Bitcoin price on halving day: Around $63,800
- Bitcoin price 150 days after the halving event: $72,000
2024 was the year that marked the approval of US-based Bitcoin ETFs, supporting the ecosystem even more than before, and marking the official institutional flow in Bitcoin-based crypto products and its recognized legitimacy as a viable hedge against inflation and digital gold.
Bull Runs Following Bitcoin Halvings: Hype, Disillusionment, Accumulation
Before the 2024 Bitcoin halving, Galaxy Digital blockchain provider made a comparison between Bitcoin’s previous halvings and its fourth one.
In the entire Bitcoin history, the coin has never reached a new ATH before the halving event. In prior cycles, halving took the coin to new heights, acting as a catalyst for its price.
In 2024, Bitcoin reached a new ATH before the halving event, suggesting that history doesn’t always repeat itself.
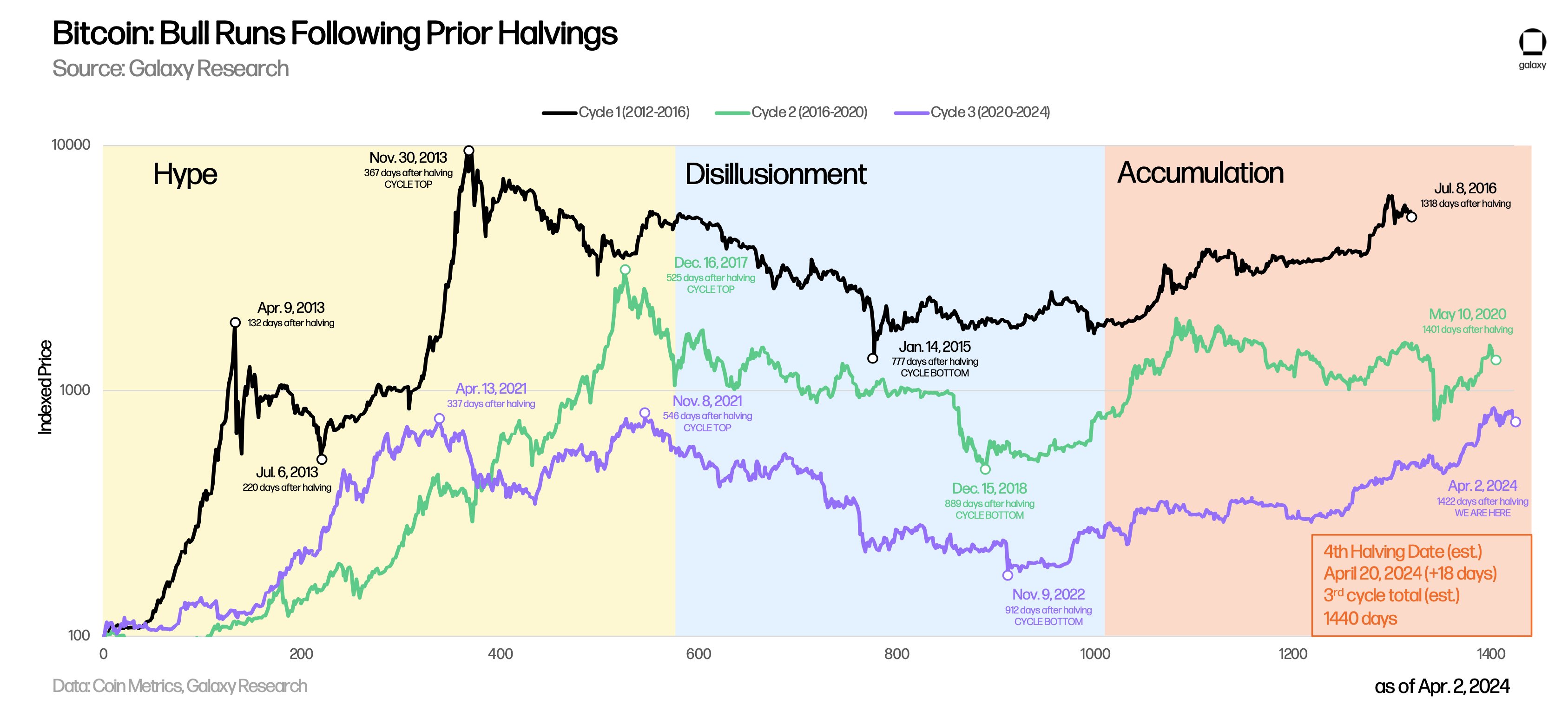
Bitcoin’s Cycle 1 (2012-2016)
- Hype Peak Post-Halving: April 9, 2013 (132 days post-halving)
- Hype Drop Post-Halving: July 6, 2013 (220 days post-halving)
- Cycle Hype Top: November 30, 2013 (367 days post-halving)
Bitcoin’s Cycle 2 (2016-2020)
- Cycle Hype Top: December 16, 2017 (525 days post-halving)
- Cycle Bottom: December 15, 2018 (889 days post-halving)
- Bitcoin Accumulation Period: Until May 2020 (1401 days post-halving)
Bitcoin’s Cycle 3 (2020-2024)
- Cycle Hype Top: November 8, 2021 (546 days post-halving)
- Cycle Bottom: November 9, 2022 (912 days post-halving)
When Is the Next Bitcoin Halving?
The next Bitcoin halving will be sometime in 2028. The exact date may vary slightly based on the actual block generation times leading up to the event.
Here are the key points of the 2028 halving that are known for sure:
- Bitcoin halving: At block 1,050,000
- Bitcoin reward per block before the halving: 3.125 BTC
- Bitcoin reward per block following the halving: 1.5625 BTC
Bitcoin halving dates will continue every four years and every 210,000 blocks mined, until all 21 million Bitcoins maximum supply is reached. The final halving is expected to happen around 2140.
Following the final halving, Bitcoin miners will primarily earn revenue via transaction fees rather than block rewards.
Why Bitcoin Halving Events Matter
There are several factors that are beneficial for the Bitcoin ecosystem due to the halving events.
1. Controlling Supply and Scarcity
Bitcoin halving places control over the supply of new Bitcoins. By reducing the number of new coins created with each block, halvings ensure a predictable and decreasing rate of supply.
The scarcity can drive up Bitcoin’s value over time, in a similar way in which scarcity affects precious metals’ value.
2. Addressing Inflation Concerns
Halving Bitcoin rewards addresses inflation concerns. Inflation is defined as a decrease in the amount of goods a certain amount of currency can buy at any given moment.
Countries have an acceptable inflation rate that is considered good for an economy, but this number is a target set by central banks as a goal, rather than a reachable figure.
Bitcoin halving was created to counter any inflationary effects on Bitcoin by:
- Lowering the miners’ rewards
- Maintaining scarcity of the coins
This inflation protection mechanism doesn’t protect Bitcoin users from the inflationary effects of fiat to which they convert Bitcoin.
3. Increasing Demand for New Bitcoins
Bitcoin halving reduces the number of new coins introduced, which triggers an increase in demand for new Bitcoins.
An increased coin demand leads to a higher price for Bitcoin.
4. Investment Opportunity
Bitcoin was not necessarily created as an investment tool and was introduced as a payment method that could remove the need for third parties and regulatory agencies.
However, investors noted that Bitcoin has the potential for gains, creating demand for the coin. Halvings represent a reduction of the new coin supply for investors, but this also offers the promise of an increase in the investment value.
5. Market Stability
Regular halvings contribute to market predictability. As investors and miners know when these events take place, they can plan accordingly.
Such predictability leads to overall market stability.
6. Mining Incentive Adjustment
Halving events trigger adjustments in the mining ecosystem, and miners must become more effective as their reward is slashed in half with each event.
The need of having to cover their operational costs leads to technological advancements and increased efficiency in the mining industry.
7. Enhanced Security
Bitcoin’s security relies on the network miners. Halving events can lead to increased Bitcoin value, and mining can become more profitable even with reduced rewards.
This can attract more miners, enhancing the network’s security via the following:
- Decentralization
- Computational power
Halving events also trigger innovation in the mining industry as miners seek more effective mining ways which include:
- More efficient hardware
- The use of AI and other new technologies
- Renewable energy sources
8. Boosting Investor Confidence
Bitcoin’s transparent and predictable nature of the halving schedule boosts investor confidence. This is achieved via acknowledging the limitation of supply.
This limitation enforced by the network’s protocol reassures investors about the long-term value of Bitcoin.
9. Promoting Hodling
The anticipation of higher prices post the halving events, encourages the holding of Bitcoin, rather than selling coins. This will also reduce the circulating supply, contributing to an upward price pressure.
How Bitcoin Halving Events Impact the Market?
Bitcoin halving events impact the market via short-term and long-term dynamics as follows:
- Short-term volatility: Price fluctuations occur due to speculative trending and market psychology, investors anticipating the reduced supply
- Long-term trends: These are shaped by the decreased rate of new Bitcoins entering circulation, fostering scarcity, and driving up prices over time.
Anticipation and price increases post-halving can reinforce bullish sentiments, influencing investor behavior and market stability.
Overall, halvings blend immediate speculation with enduring economic fundamentals.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What Is Bitcoin Halving?
Bitcoin halving is an event that occurs approximately every four years when the miners’ reward is slashed in half.
Why Does Bitcoin Halving Happen?
Bitcoin’s halving is an event programmed into the Bitcoin protocol to ensure a finite supply of 21 million Bitcoins. The mechanism helps control inflation, by decreasing the rate at which new coins enter circulation, among others.
When Was the First Bitcoin Halving?
The first Bitcoin halving occurred on November 28, 2012, at block number 210,000. The event slashed miners’ rewards from 50 BTC to 25 BTC.
When Is the Next Bitcoin Halving Date?
The next Bitcoin halving date will be sometime in 2028. The event will occur at block number 1,050,000, and it will slash miner rewards from 3.125 BTC to 1.5625 BTC.
How Bitcoin Halvings Affect the Price of BTC?
Historically, Bitcoin halvings have been follo3wed by significant price increases for Bitcoin. This can however vary according to market conditions, investor sentiment, and other factors.
Can Bitcoin Halvings Cause Network Issues?
Bitcoin halvings can impact miners’ incentives, and this can potentially affect network security if mining becomes less profitable. However, according to history, the network has adjusted with miners finding innovative ways to adapt to reduced rewards via technological advancements, renewable energy sources, and more.
As a conclusion, Bitcoin halving dates are important events in the Bitcoin ecosystem and the entire crypto industry as they historically led to Bitcoin becoming a scarcer and more valuable asset.
Bitcoin halvings have important network implications. For miners, these events might result in the consolidation of their ranks as individual or weaker miners drop out of the mining ecosystem due to a lack of efficiency.
So far, there have been four halvings for Bitcoin, and each and every one of them contributed to increased interest and worldwide adoption of Bitcoin as a store of value, a hedge against inflation, and a payment tool.









